How To Add User to Sudoers & Add User to Sudo Group on CentOS 7
The sudo command stands for “Super User DO” and temporarily elevates the privileges of a regular user for administrative tasks. The sudo command in CentOS provides a workaround by allowing a user to elevate their privileges for a single task temporarily.
This guide will walk you through the steps to add a user to sudoers in CentOS.
Prerequisites
- A system running CentOS 7
- Access to a user account with root privileges
Add User to Sudoers on CentOS
Step 1: Login as Administrator
If you’re working on a local machine, log in to the system with administrator credentials.
If you’re connecting to a remote machine (over a network), open a terminal window and enter the command:
The server_ip_address is the network IP address of the server you’re logging into. Enter your credentials when prompted.
Step 2: Create a New Sudo User
To add a new sudo user, open the terminal window and enter the command:
Use the actual username for your new user in place of UserName.
Next, create a password for the new user by entering the following in your terminal window:
How to Add Users to Sudo Group
By default, CentOS 7 has a user group called the “wheel” group. Members of the wheel group are automatically granted sudo privileges. Adding a user to this group is a quick and easy way to grant sudo privileges to a user.
Step 1: Verify the Wheel Group is Enabled
Your CentOS 7 installation may or may not have the wheel group enabled.
Open the configuration file by entering the command:
Scroll through the configuration file until you see the following entry:
If the second line begins with the # sign, it has been disabled and marked as a comment. Just delete the # sign at the beginning of the second line so it looks like the following:
Then save the file and exit the editor.
Step 2: Add User to Group
As usual, replace UserName with the name of the user receiving sudo privileges.
Step: 3 Switch to the Sudo User
Enter the password if prompted. The terminal prompt should change to include the UserName.
The terminal should request the password for UserName. Enter it, and you should see a display of the list of directories. Since listing the contents of /root requires sudo privileges, this works as a quick way to prove that UserName can use the sudo command.
Alternative: Add User to Sudoers Configuration File
If there’s a problem with the wheel group, or administrative policy prevents you from creating or modifying groups, you can add a user directly to the sudoers configuration file to grant sudo privileges.
Step 1: Open the Sudoers File in an Editor
This will open the /etc/sudoers file in a text editor.
Step 2: Add the New User to file
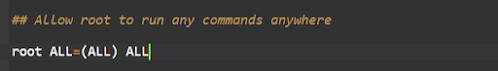
Scroll down to find the following section:
Right after this entry, add the following text:
Replace UserName with the username you created in Step 2. This section should look like the following:
Save the file and exit.
Step 3: Test Sudo Privileges for the User Account
Switch user accounts with the su (substitute user) command:
Enter the password for the account, if prompted. The terminal prompt should change to include UserName.
List the contents of the /root directory:
Enter the password for this user when prompted. The terminal should display a list of all the directories in the /root directory.
Conclusion
This guide showed you how to add a user to sudoers in CentOS or modify the privileges of an existing sudo user.






Comments
Post a Comment